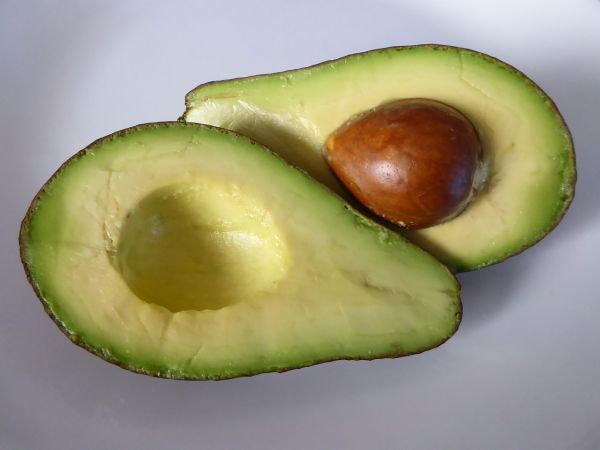
Avocado is considered a superfood and can be very beneficial for our health. We reach for this butter fruit more eagerly every day. Despite the high caloric value, due to the large amount of fat, avocado shouldn’t be avoided. Paradoxically, this fruit helps in weight loss and lowers bad cholesterol levels. It is a rich source of vitamins and minerals essential for the growth and health. In the kitchen we can use it in many ways – as a healthier substitute for butter or as a bread spread, but also as an ingredient of many salads. Monounsaturated fatty acids present in avocados protect our heart, therefore it is advised to be used instead of butter.
WHY AVOCADO
Avocado has a bad reputation because of high caloric value and fat content – approximately 85% of the calories are fatty acids. However, the fat contained in the avocado is largely monounsaturated fatty acids with unique healing properties!
One avocado (approx. 140-150g) added to salads, improves significantly the absorption of many minerals and vitamins. Recent studies have shown that when added to salads containing spinach, lettuce and carrots, it improved absorption of beta-carotene and lycopene (the two main antioxidants) by 200-400%!

CALORIC VALUE
Average avocado weighs 215 g. On the other hand edible portion (without seeds) weighs 140g.
100 g of fruit are (source – Wikipedia):
- Calories: 221 kcal
- Carbohydrates: 0,4 g
- Protein: 1,9 g
- Fat: 23,5 g (mostly monounsaturated)
- Fiber: 6,3 g
- Water: 66%
- Vitamins A, B1, B2, C, E, PP, K and H, pantothenic acid
- Minerals: calcium, potassium and phosphorus
NUTRITIONAL VALUES
- Phytosterols have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Unsaturated fatty acids (oleic acid, linoleic acid), and fiber – protect biological membranes of cells, intensely hydrate the skin and improve the immune system. Both components also give a feeling of satiety and help reducing weight. Average avocado contains approx. 6g dietary fiber (soluble and insoluble).
- Vitamins – K, B6, C, folic acid that prevent diseases, allergies and regulate the blood pressure.
- Trace elements – potassium and copper, which control muscular and myocardial contraction, improve concentration.
- carotenoids and lutein – protect eyesight that inevitably deteriorates with age.
- Squalene – has antibacterial and antifungal properties. It prevents ischemic heart disease and slows the aging process.
- Pantothenic acid – lowering bad cholesterol (LDL) while lifting HDL, or good cholesterol.
- Protein – avocado is a good source of vegetable protein, which is important for vegetarians and vegans. It consists of approx. 10 thousand different proteins and is a good muscle building material.
HOW TO PEEL AVOCADO
- Cut the washed avocado along in two halves
- Turn both avocado halves in opposite directions
- After turning, avocado avocado separates easily and the pit stays in one half
- Give the pit a thwack with a sharp knife and remove it (keep the pit if you want to make a guacamole)
- Scoop out the pulp
HOW TO USE
Avocado is widely used in many cuisines all over the world. The most popular ways to use avocados are:
- Guacamole – avocado spread
- vitamina de abacate – brasilian drink, a smoothie made of avocado, milk and sugar
- ingredient of salads
- avocado puree as an addition to pasta or filling for dumplings
- cold awokado soup
- vegetarian sushi

If You find this article interesting, please share It using the social media buttons under the article. If you don’t want to share it, maybe at least like it? :-)